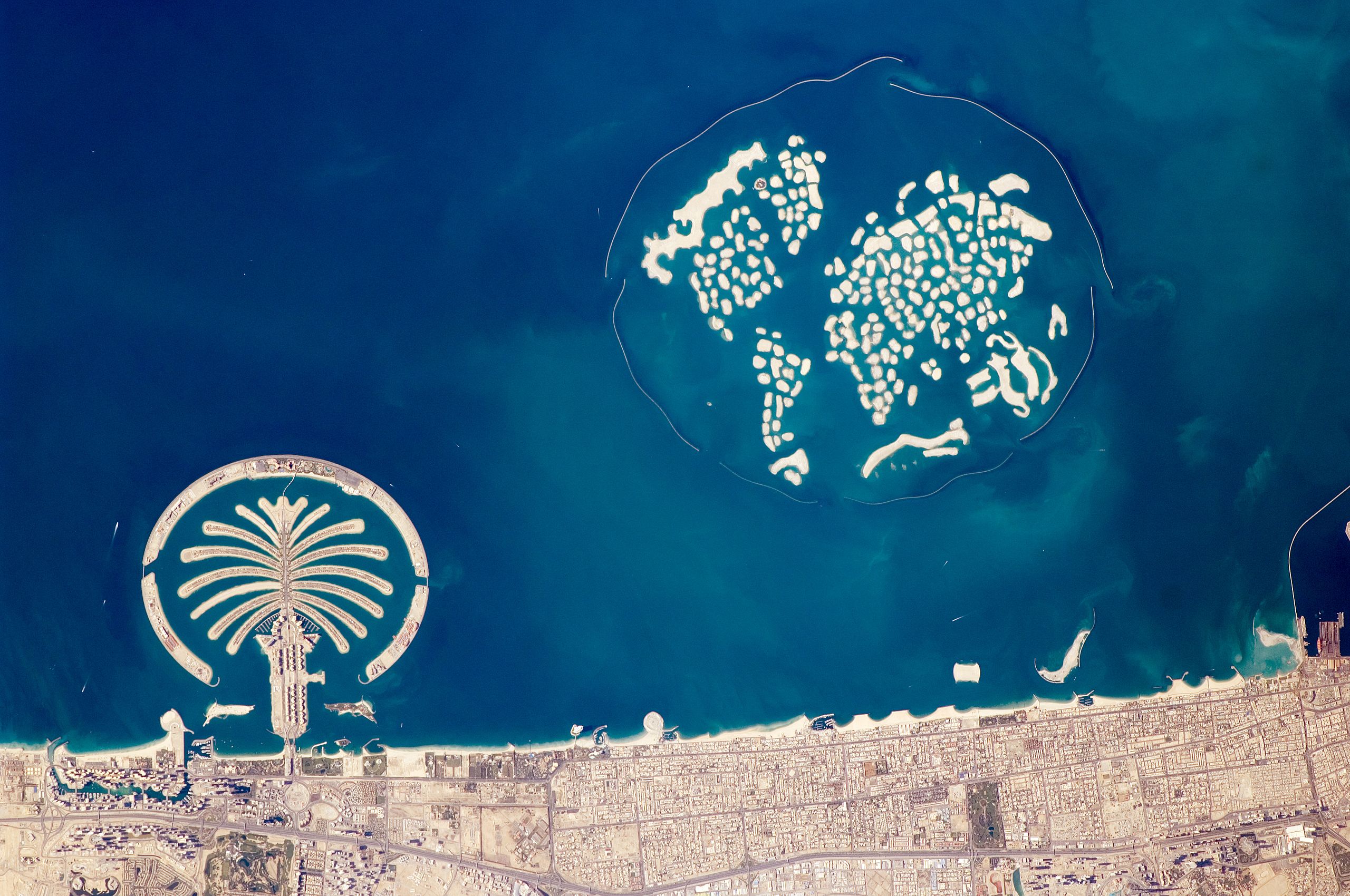
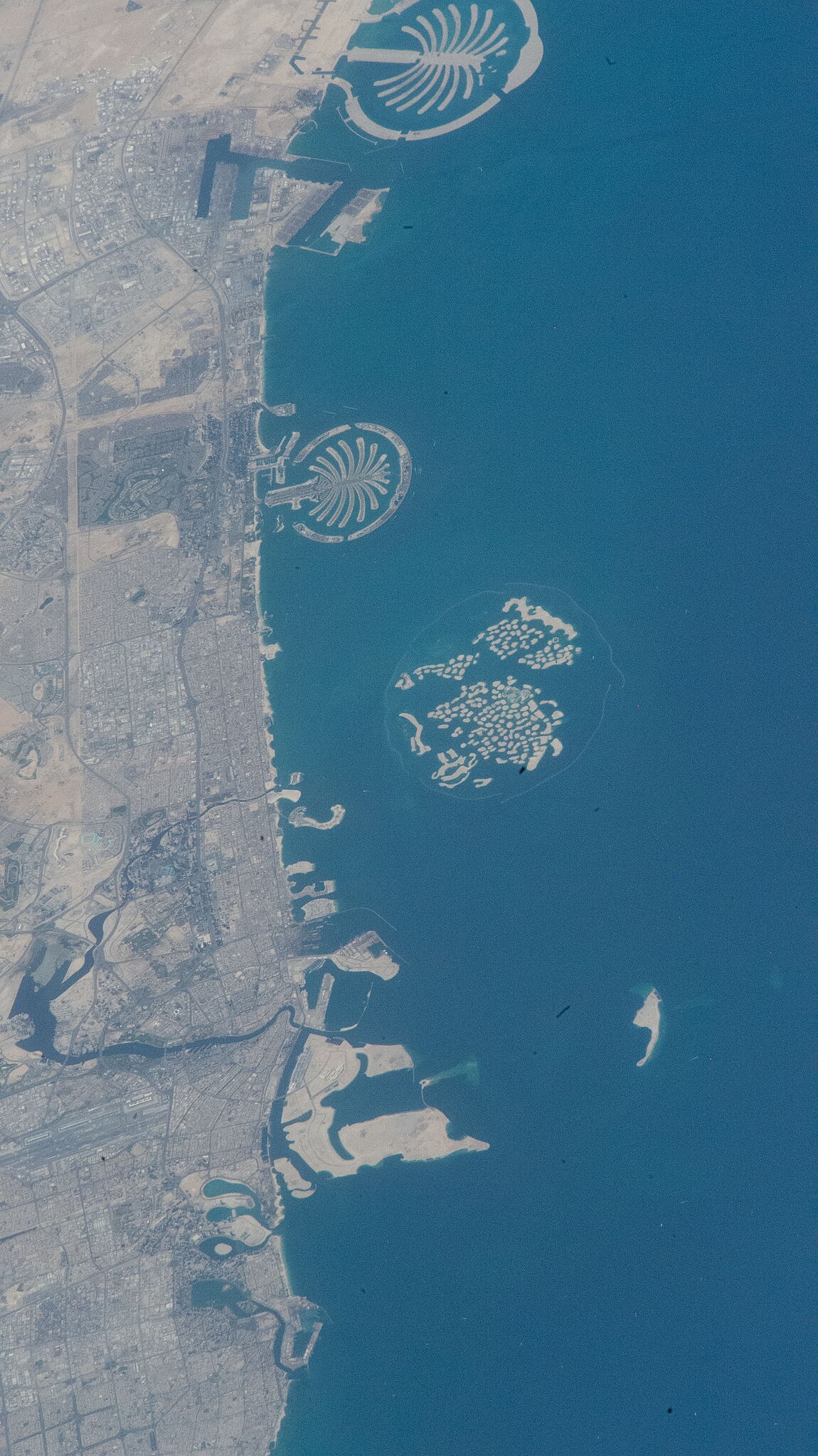
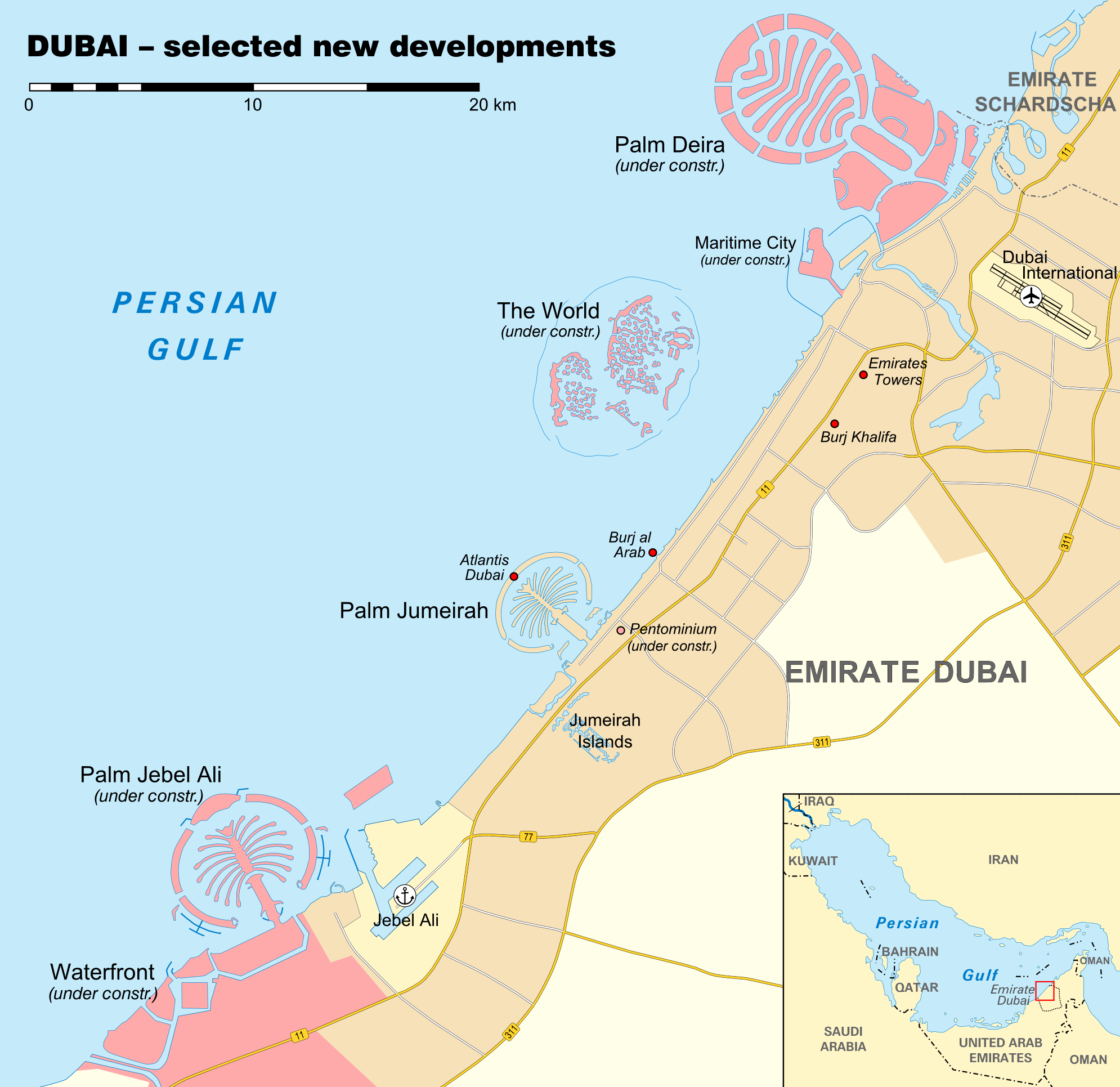
Dubai epitomises the Gulf’s property market. It did suffer a massive correction back in 2009 (Collinson, 2009), the Emirate needed to borrow several billion from Abu Dhabi (Davidson, 2009) but, that debt has been repaid and today the sector is once again booming (Maccioni, 2024).
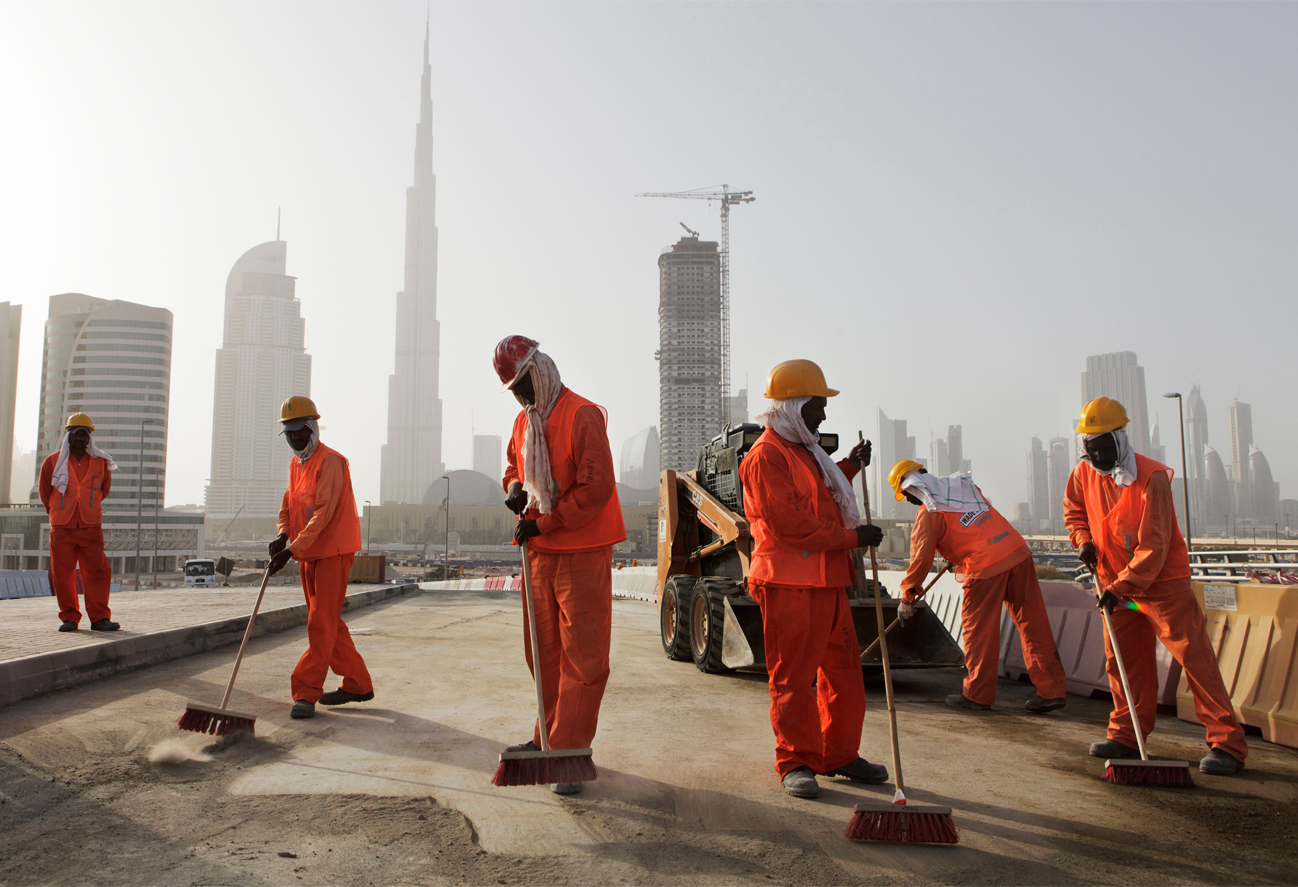


A dream foreclosed (?)
The following was penned by Davidson in 2009; at the tail-end of the 2003–2008 period in the Emirate of Dubai (UAE) which was described by Bertrand (2012) as “the world’s most massive real estate bubble.”
Glitzy Dubai, long considered the new Monte Carlo or the Las Vegas of the Middle East, has suffered one of the worst crash landings of this global recession. Dubai might be considered a bellwether of the global credit crunch. Until recently touted as a beacon of progress in an otherwise unstable region, the tiny emirate’s seemingly innovative economic and political model is now unravelling, with no end in sight to the uninterrupted stream of bad news. Construction has ground to a shuddering halt, unemployment is rising, sovereign debt is exposed, lawsuits are being prepared, and the population is decreasing, as those who moved to Dubai in search of a better life have either lost their jobs or are cutting their losses and leaving. To make matters worse, as the city empties itself out, traffic thins, and cars and credit cards are abandoned at the airport, the embattled authorities have embroiled themselves in fresh controversies by introducing protectionist policies for their citizens and a new media law that forbids criticism of the economy, and earning Dubai an anti-Semitic branding in the sports world by denying a visa to an Israeli athlete. With investor confidence in tatters and debt repayments looming, its humiliated rulers have had little choice but to turn to their wealthier neighbors. But although help has finally arrived, it is by no means the lifeline that the emirate really needs, and Dubai’s future hangs in the balance.
Only time will tell for history is history (unendingly so). The digitisation of everything is as good as it is bad. One’s predictions and forecasts, with hindsight and internet indexing, can come to be seen as having been too hubristic (one could counter that they were just thinking and writing in a heuristic fashion).
In the same year as Davidson wrote the above, Lewis (2009) said the following. “A six-year boom that turned sand dunes into a glittering metropolis, creating the world’s tallest building, its biggest shopping mall and, some say, a shrine to unbridled capitalism, is grinding to a halt.” And that, “half of all the UAE’s construction projects, totalling £400 billion, have either been put on hold or cancelled, leaving a trail of half-built towers on the outskirts of the city stretching into the desert.”
Red hot (once more)
In a recent piece for the London-based Financial Times, it was said that if you want to “escape the global gloom, just take a flight from its epicentre, London, to any leading capital of the Gulf” Sharma (2022). “Dubai is enjoying yet another real estate boom. Regional rivals like Riyadh are racing to be the next Dubai, funnelling oil profits into property mega-projects.” Sharma also suggests that many of the Gulf leaders do “recognise that a boom built on high oil and property prices is unlikely to endure, but that age-old problem can wait.”
In 2023 The Economist wrote that while Dubai’s property market has much to recommend it (low taxes and a large pool of renters), some wonder if the sector, “the backbone of Dubai’s economy, is again becoming a bubble.” The Emirate has already endured two real estate crashes this century: “an abrupt one during the financial crisis in 2008, when property values fell by half, and a slower one from 2014 to 2020, when they slid by 35 per cent.”
📕 “Money, Markets & (Gulf) Monarchies” →
References
Bloch, R. (2010). Dubai’s Long Goodbye. International journal of urban and regional research, 34(4), 943–951. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-2427.2010.01014.x
Collinson, P. (2009, May 26). Dubai suffers biggest house price slump. The Guardian. https://www.theguardian.com/money/2009/may/26/dubai-property-crash
Crisp, J., & Corfe, O. (2023, December 9). Inside the luxurious lives of the Russians of Dubai. The Daily Telegraph. https://www.telegraph.co.uk/world-news/2023/12/09/inside-the-luxurious-lives-of-the-russians-of-dubai/
Davidson, C. (2009). Dubai: foreclosure of a dream. Middle East report, 251(Summer), 8–13. https://www.jstor.org/stable/27735295
Lewis, P. (2009, February 13). Dubai’s six-year building boom grinds to halt as financial crisis takes hold. The Guardian. https://www.theguardian.com/world/2009/feb/13/dubai-boom-halt
Hanieh, A. (2018). Money, Markets, and Monarchies: The Gulf Cooperation Council and the Political Economy of the Contemporary Middle East. Cambridge University Press.
Maccioni, F. (2024, July 8). Dubai property market stays strong as demand from ultra-rich continues. The Independent. https://www.independent.co.uk/news/world/middle-east/dubai-property-market-luxury-homes-b2575845.html
Renaud, B. (2012). Real Estate Bubble and Financial Crisis in Dubai: Dynamics and Policy Responses. Journal of real estate literature, 20(1), 51–78. https://doi.org/10.1080/10835547.2012.12090313
Sharma, R. (2022, November 21). The Gulf is partying while it can The Financial Times. https://www.ft.com/content/740703ba-96b2-43d1-af9e-848cec61f1ec
The Economist. (2018, September 27). Sweet deserts. The Economist, 428(9111), 58. https://www.economist.com/international/2018/09/27/how-the-united-arab-emirates-became-an-oasis-for-tax-evaders
The Economist. (2022, September 24). Boom time in the Gulf. The Economist, 444(9314), 14. https://www.economist.com/leaders/2022/09/22/an-energy-crisis-and-geopolitics-are-creating-a-new-look-gulf
The Economist. (2022, September 24). Entrepotluck. The Economist, 444(9314), 68–69. https://www.economist.com/finance-and-economics/2022/09/22/dubai-is-the-worlds-resurgent-entrepot
Troianovski, A. (2023, March 15). ‘Russia Outside Russia’: For Elite, Dubai Becomes a Wartime Harbor. New York Times. https://www.nytimes.com/2023/03/13/world/europe/russia-dubai-ukraine-war.html