Rutledge, E. J. (2018, May 10). Giving private sector jobs the required significance. Gulf News. https://gulfnews.com/business/analysis/giving-private-sector-jobs-the-required-significance-1.2218799

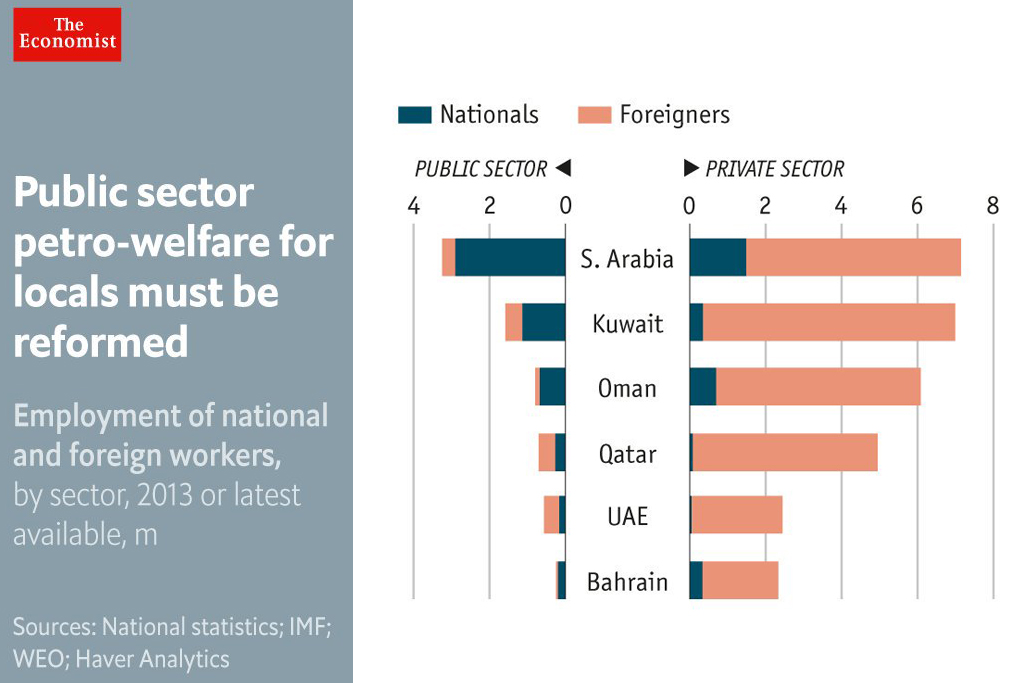
The Federal Authority for Government Human Resources gave research on Emiratisation a boost by launching an annual award for scholarly work on the UAE labour market and human resources. This is a timely incentive because oil prices seem destined to remain some way off on their 2010—14 highs, and comfy government jobs are said to be a thing of the past.
Among the wining studies was one conducted by the UAE University; it was the first large-scale study to investigate the views of UAE nationals working in the private sector and polled 653 individuals. The survey included questions related to job satisfaction and also on context-specific sociocultural sentiments such as the prestige attached to a public sector job.
Indeed the UAE’s labour market’s distortions and segmentations cannot be fully understood, let alone addressed, without such issues being factored into the equation.
The research found that it was “salary and benefits” that most significantly and positively predicted the intention of Emiratis to continue working in the private sector, while “sociocultural influences” — societal attitudes on a given occupation’s prestige and status level — had the most significant negative effect and was likely to deter Emiratis from staying in the private sector.
In other words, money does still talk. However, employee satisfaction isn’t all about money, “training opportunities” and the “nature of job” also writ large. The latter finding is of importance because it implies, at the very least, that today’s graduates do see private sector occupations as more interesting and fulfilling, if compared to the more bureaucratic-style ‘classic’ public sector jobs.
However, as evidenced by the research, it continues to be the case that “classic” public sector positions continue to attract the most status and prestige. This sentiment is even more pronounced among male employees, with male respondents significantly more likely to be adversely affected by sociocultural influences (the pride or prestige attached to public sector positions) and be less happy with the nature (or “environment”) of work in the private sector.
The research has applied policy relevance. The more closely aligned like-for-like public/private sector positions become in terms of salaries, working hours and days of annual leave, the more attractive will be private sector career paths. Such alignment — most likely by way of more extensive subsidies or top-ups for nationals working in the private sector — would help redress the current notion that it is the citizens who’ve secured government jobs that have the higher status. The findings also show that internship programmes — that are now compulsory at some federal universities — are paying dividends and recommends that more interns should be placed in the private sector as about one-third of those surveyed were working for private sector companies where they had completed their internships.
Another revealing find was the fact that almost three-quarters of the sample of UAE nationals employed in the private sector currently had other members of their immediate family working in the same sector. Therefore government policy that champions those Emiratis who take up non-conventional private sector career paths will help change prevailing societal attitudes in relation to what is, and is not, considered a suitable career path for Emiratis.
The study on private sector Emiratisation by Dr Emilie Rutledge and Dr Khaled Al Kaabi recently received the Federal Authority For Government Human Resources Award for the Best Academic Research in HR. Their study is timely in that it considers this topic in an era where comfy government jobs are said to be a thing of the past. In addition to this, their survey-based research—polling 653 individuals—is the first large-scale one to investigate the sentiments of UAE nationals actually working in the private sector. While basing their research on the notions of the Theory of Planned Behaviour and job satisfaction scales, they also factor in what are termed as context-specific sociocultural sentiments. They make the case that the UAE’s labour market distortions and segmentations cannot be fully understood, let alone addressed, without such issues being factored into the equation. As Dr Rutledge says, “employee satisfaction isn’t all about money, the benefits of even the nature of the work and relations with fellow workers, societal attitudes on a given occupation’s prestige and status levels also writ large.” As evidenced by their findings and analysis, it continues to be the case that ‘classic’ public sector positions continue to attract the most status and prestige. This sentiment is even more pronounced amongst the male survey participants.
Another issue that the study highlights is the difficulty face in defining exactly what constitutes the private sector. In a region who’s labour markets are characterised by being highly distorted and segmented along public/private and national/non-national employee lines, the division between public and private entities is often hard to determine. As Dr Al Kaabi explains, it was necessary for their study to include government-backed entities as quasi-private ones as this is what society considers them to be. While some labour market economists would classify these within the government sphere, in the UAE at least, many in this category are commercially-run and, “really do now manage their human resources as if they were genuine private sector operators.”
The study found that it was ‘salary and benefits’ that most significantly and positively predicted continuance intentions (β = .399, p < .001) while ‘sociocultural influences’ most significantly and negatively predicted continuance intentions (β = -.423, p < .001). In other words, money does still talk. These observations also suggest that the more closely aligned like-for-like public/private sector positions become in terms of salaries, working hours and days of annual leave, the more attractive will be the private sector career paths. The authors of this study both contend that such alignment—most likely by ay of public sector pay freezes than pay cuts—would help redress the current notion that it is the citizens who’ve secured government jobs that have the higher status. Other job satisfaction related constructs that had a significant impact on the degree to which individuals planned to continue working in the private sector were: ‘training opportunities’ were a positive factor (β = .163, p < .001) and interestingly, the ‘nature of job’ (β = .072, p .009). The latter finding is of importance because it implies, at the very least, that today’s graduates do see private sector occupations as more interesting and fulfilling (if compared to the more bureaucratic-style ‘classic’ public sector jobs).
In terms of differences between the genders, male respondents were significantly more likely to be adversely affected by sociocultural influences pride (or “prestige) and were significantly less happy with the nature (or “environment”) of work in the private sector. With regard to age, the younger the respondent, the less likely they will be to intend to continue working in the private sector. The study’s authors argue that younger members of society are significantly more influenced by sociocultural barriers and least satisfied with the professional development opportunities on offer. They suggest that this may be due to the fact that they have relatively junior positions at the given private sector organisation. With regard to education, the higher one’s qualification is the more likely it will be that they intend to remain in the private sector. This ties in with the age-related differences, it follows that within the private sector the positions that require post-graduate qualifications will not only pay more but will also have attached to them more status.
Of perhaps most note and applied policy relevance are the following observations. Firstly, no less than one-third of those surveyed were working for private sector entities that they had actually competed their internships with. This suggests that the internship programs that are now compulsory at some federal universities in the UAE are paying dividends. The second observation is that almost three-quarters of the sample (that is UAE nationals employed in the private sector) currently have other members of their immediate family working in the same sector. As Dr Rutledge says, “any government policy that champions those individuals who take up non-conventional career paths will help change prevailing societal attitudes and norms in relation to what are and are not suitable career paths.”